Upload Google Photos 400 Bad Server Easy Photo Scan
Sep 27, 2022
Leonardus N.
8min Read
How to Fix a 400 Bad Request Error: 8 Easy Methods

The 400 bad request error is an HTTP status code that describes an error caused by an invalid request. Thus, the server can't understand and process it. Most HTTP error 400 bad requests are caused by malformed request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing.
Download eBook: Build Your First Website in 9 Easy Steps
If you're browsing the internet and encounter this error, it's possible to solve the problem easily. However, there are several occasions when the error comes from the website server. In this case, only the site owner can fix the problem.
This article will discuss eight methods of resolving a 400 bad request error. We will also cover the HTTP error 400 bad request message variations and their possible causes.
| Error code | 400 Bad Request Error |
| Error type | Client-side |
| Error variations | HTTP Error 400 HTTP Error 400 – Bad Request HTTP Error 400. The request hostname is invalid HTTP Status 400 – Bad Request 400 Bad Request 400 – Bad Request. The request could not be understood by the server due to malformed syntax. The client should not repeat the request without modifications. 400 Bad Request. Request Header Or Cookie Too Large Bad Request – Invalid URL Bad Request – Error 400 Bad Request – Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand |
| Error causes | Bad URL syntax File too big Bad cookies or cache DNS issues |
Variations of the 400 Bad Request Error
As an HTTP status code, the 400 bad request error informs users why they can't access a web page. That said, the error message may vary or not show the error code itself.
Here are some variations of the 400 bad request error message you may encounter:
- HTTP Error 400
- HTTP Error 400 – Bad Request
- HTTP Error 400. The request hostname is invalid
- 400 Bad Request
- 400 – Bad Request. The request could not be understood by the server due to malformed syntax. The client should not repeat the request without modifications.
- 400 Bad Request – Request Header Or Cookie Too Large
- Bad Request – Invalid URL
- Bad Request – Error 400
- Bad Request – Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand
"400 Bad Request Error" on Different Browsers
Just like a 404 error page, the 400 bad request page is customizable. For example, Google has a custom 400 bad request error page that looks the same on all web browsers.
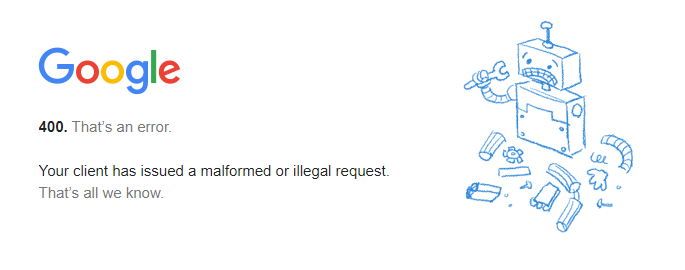
However, if the site doesn't have a customized error page, the web browser will show the default one. Here is how the HTTP 400 bad request status code looks on different browsers:
Google Chrome
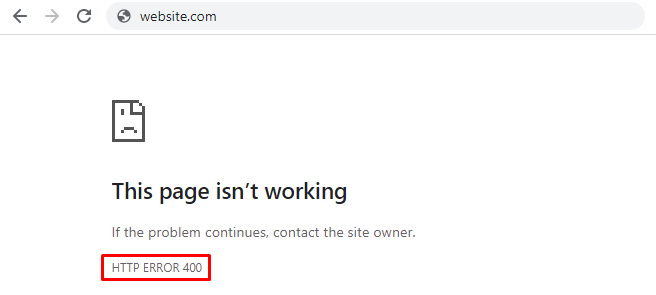
For 400 bad request, Chrome will show an error icon with The page isn't working text followed by If the problem continues, contact the site owner. Then, you'll find the HTTP ERROR 400 at the bottom of the message.
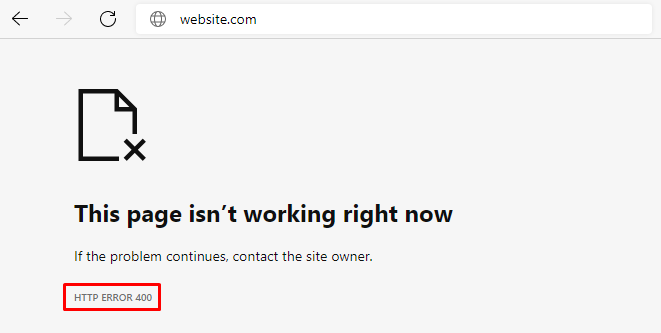
Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge has a design almost identical to Google Chrome's, with the HTTP ERROR 400 text at the bottom.
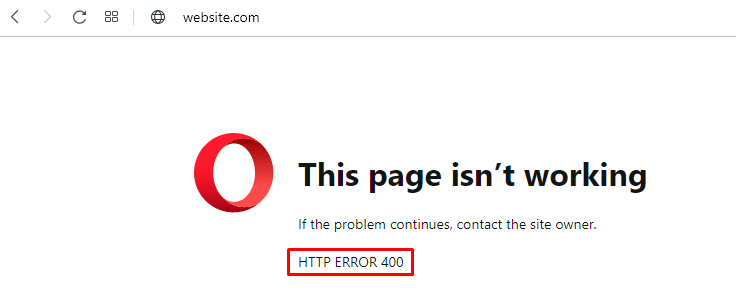
Opera
The HTTP 400 bad request error in Opera displays the same text as Google Chrome. The only difference is the icon, as Opera uses its logo.
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox will show a blank page when you try to access a website using the wrong syntax. There's no text indicating that you encountered an HTTP 400 bad request error, which makes identifying the problem harder.

Safari
Like Mozilla Firefox, the browser will appear blank with no indication of the HTTP 400 bad request error.
Causes of the 400 Bad Request Error
When you try to access a website, your computer sends a request to the web server. Then, the server processes the request and sends back the page you want.
The error 400 bad request happens when the server can't understand the request. Thus, it won't process it and will send you the error code instead.
In most cases, client-side issues trigger the error. Some common causes of the 400 bad request error are:
- Malformed URL syntax – the URL may contain invalid characters such as {, }, [, or ]. A wrongly encoded URL can also contain wrongly used ASCII characters, such as double percentage characters.
- Large file size – websites have a file upload limit. An attempt to upload a file that exceeds this limit can be considered a bad request and trigger the HTTP 400 error status code.
- Corrupted browser cookies or cache – expired cookies or corrupted browser cache may interfere with the request and trigger the error. This commonly happens on login pages such as the WordPress login page.
- Bad DNS cache – if the website has moved to a new domain name or web host, the DNS cache data in your operating system may be invalid.
How to Fix a 400 Bad Request Error
The first action we recommend is refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, then you should try the following methods.
1. Double Check the Domain Address
One of the most common causes of HTTP status 400 bad request error is a wrong URL. This may include a mistyped URL, malformed syntax, and illegal characters in the URL.
It's easy to mistype a URL, so be sure to check the domain name spelling. If the URL contains a directory path, file name, or query string, pay attention to special symbols such as a hyphen (-) or percentage character (%).
For example, www.hostinger.com/tutorials is the correct domain name. If you type in www.hostinger.com/%tutorials in the URL bar with an extra percentage character, it will result in a 400 bad request error.
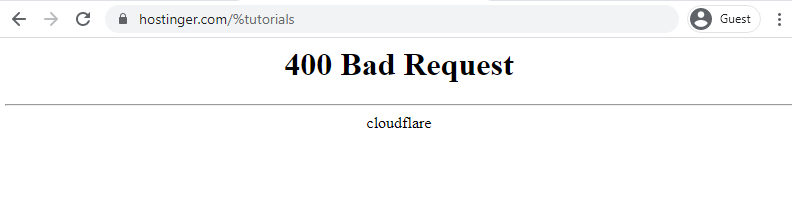
A badly encoded URL can also cause this error. URL encoding converts characters into ASCII characters to make them transferable on the internet. For example, one of the most common encodings is replacing space with %20.
However, a URL can be encoded incorrectly and thus contain incorrect syntax, like double percentage characters (%%). If you enter a URL or click on a link that's badly encoded, you'll end up with a bad request error 400.
When encountering a 400 bad request error because of a wrong URL, use an encoder/decoder tool. Decode the URL and encode it again to make sure it is correct.
2. Search the Keyword
There may be cases where you are sure that the URL is correct, yet the error persists. If you know the title of the article or page you're looking for, search the keywords on the website or a search engine. Sometimes you can even see the title on the URL.
For example, in the /tutorials/how-to-make-a-website URL, you'll see the article's title at the end of the URL. If the website has a search feature, type the keyword to find the article.
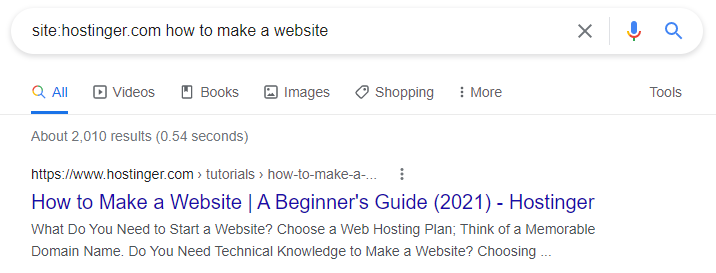
Alternatively, use a search engine like Google or Bing. To perform a search on a specific site, type site: followed by the website's URL and the keyword.
For example, the title of the article is how to make a website. Therefore, you type site:hostinger.com how to make a website.
3. Clear Browser Cache or Cookies
Browser cookies and cache store site data and content on the client's side to improve the browsing experience.
The browser cache contains website files such as texts and images to reduce requests to the web server and make the page load faster. At the same time, cookies store the user's session history and preferences to make personalized browsing possible.
However, cookies may expire after some time. Also, both the website cookies and cache can be corrupted and cause a 400 bad request error.
Additionally, HTTP status 400 bad request error can happen when the web browser sends cookie data that's too large. In this case, the error message appears as 400 Bad Request – Request Header Or Cookie Too Large.
Try clearing your browser cache and cookies to solve this problem. If you're using Google Chrome, here are the steps to do it:
- Click on the three dots on the top right corner of Google Chrome and select Settings.
- Find the Privacy and security section and click on Clear browsing data.
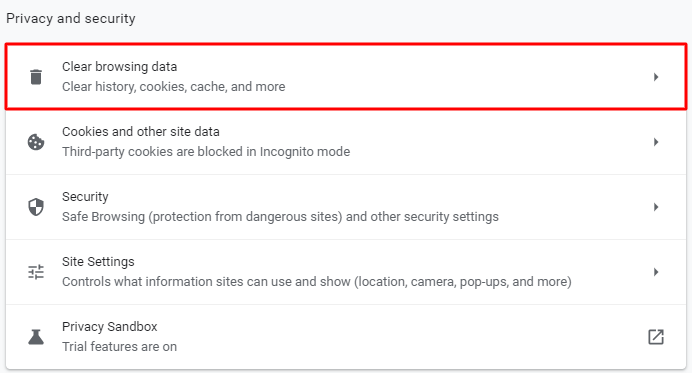
- On the Clear browsing data window, check the Cached images and files and Cookies and other site data and use the drop-down menu to select the time frame.
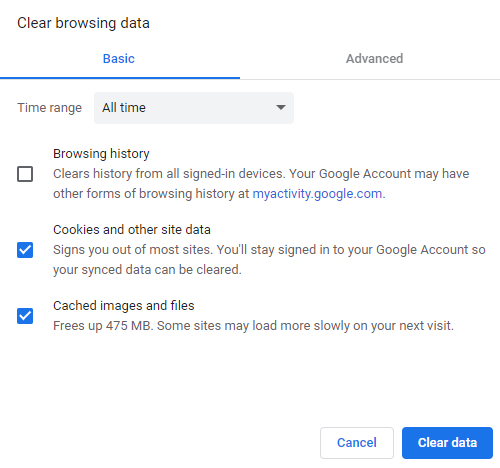
- Click Clear data and restart Google Chrome to finish the process.
Remember that clearing the browser cache and cookies resets the settings and signs you out of websites you've visited. Also, it will take more time to load the websites since the browser will need to retrieve the content previously stored in the cache.
If the cache and cookies were causing the 400 bad request error, you should be able to visit the website normally again. However, if it doesn't work, try the next method.
4. Turn Off Browser Extensions
Browser extensions can also cause a bad request error 400. That's because these extensions interfere with the request sent to the web server, which may lead the web server to interpret the request as invalid.
Moreover, browser extensions may affect cookies, which leads to a 400 bad request error. To find out if a browser extension is causing the problem, we recommend disabling all extensions first. Here are the steps for Google Chrome:
- Click on the three dots on the top right corner of Google Chrome. Select More tools -> Extensions.

- Turn off all extensions individually by clicking on the switch button.

- Refresh the web page. If it loads normally, one of the extensions is causing the 400 bad request error.
After establishing that one of the extensions triggered the error, you need to identify the exact extension. Turn on the extensions one by one, refreshing the web page each time.
If you encounter a 400 bad request error after turning on one of the extensions, you've found the one causing the error. Keep the extension disabled or remove it altogether by clicking the Remove button on the extension settings page.
5. Check the File Size
Trying to upload a file that exceeds the server file size limit might trigger an HTTP status 400 bad request error. Sites usually have a different file upload limit, so check if the file you want to upload fits the limit.
If the website doesn't mention the file limit, upload a small file to check whether that's causing the error. If it works, then you should resize the file you originally wanted to upload.
Keep in mind that file compression may negatively affect its quality. If it's a PDF or image, it can make the content blurry and unreadable. Be sure to check the quality of the file after compression and make sure that it's still acceptable.
There are many free online compression tools so that you don't need to install additional software on your computer. Some of the great examples are HiPDF for PDF files and UniConverter for video and audio files.

6. Flush DNS Cache
When you visit a site for the first time, the system goes through a DNS lookup, which searches for the nameservers and IP addresses that are associated with the domain name.
Your operating system then stores the IP addresses of the web servers in the DNS cache. Therefore, the system can reduce the DNS lookup process on the next visit, making the site load faster.
However, a corrupted or outdated DNS cache can trigger the HTTP error 400 bad request. In this case, you need to flush the DNS cache.
Since the DNS cache is stored in the operating system, the methods to flush it may vary. If you use Google Chrome, you'll also have to flush the DNS cache in the web browser.
Here are the steps to do it on Windows and Mac OS:
Microsoft Windows 10
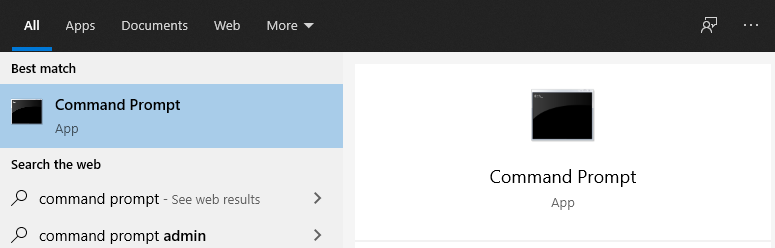
- Right-click on the Windows Start Menu and select Search or use the search box in the taskbar if enabled.

- Type command prompt and select the Command Prompt application.
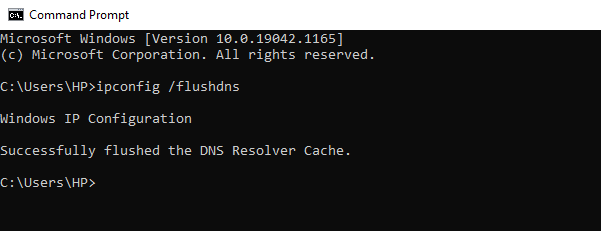
- Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.
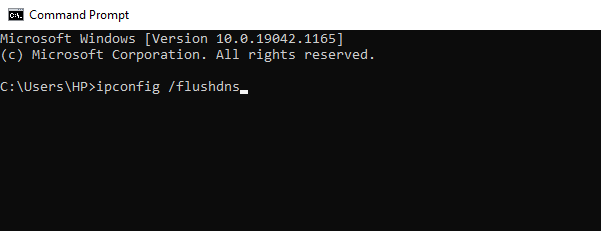
- You'll see the Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache message after the process is completed.
macOS X
Press the F4 key to open Launchpad and enter Terminal to open the command terminal. Run the following command if you use macOS Sierra, X El Capitan, X Mavericks, X Mountain Lion, or X Lion:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder.
Google Chrome
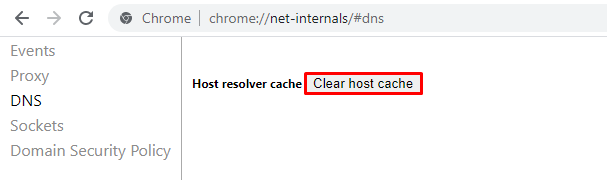
- Type chrome://net-internals/#dns on Google Chrome's address bar and press Enter:
- Click Clear host cache.
If you use a different operating system, make sure to check our comprehensive guide on how to flush DNS cache.
7. Contact the Site Owner to Report the Error
If all attempts to fix the 400 bad request error didn't work, there's a possibility that the problem isn't a client error but rather is a misconfiguration that the web owner needs to fix.
In this case, try to visit the contact page of the website and fill a contact us form, if available. Otherwise, most sites also have contact email addresses and social network accounts where you can inform them about the 400 bad request error.
8. Restart Your PC and Other Hardware
The last method is to restart your computer and network connection hardware, such as router and modems.
Restarting a PC often solves various problems, including the 400 bad request error because it clears the Random Access Memory (RAM). Moreover, it flushes the temporary cache that's created as you open and close programs.
Temporary data from background processes may interfere with the request sent to the server, causing the 400 bad request error.
Conclusion
The HTTP status 400 – bad request indicates that the request sent to the server is invalid or corrupted. Just like other 4xx status codes, a 400 bad request is a client-side issue.
It can be caused by malformed request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing.
Since this is a client-side problem, users can easily resolve most of the 400 bad request errors. To recap, here are eight methods to resolve the error:
- Double-check the domain address.
- Search the keyword.
- Clear browser cache and cookies.
- Turn off browser extensions.
- Check and reduce the file size.
- Flush the operating system's DNS cache.
- Report the error to the site owner.
- Restart the PC and networking equipment such as the router and modem.
If you have other tips or solutions, feel free to leave us a comment below.
Source: https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/how-to-fix-400-bad-request-error
0 Response to "Upload Google Photos 400 Bad Server Easy Photo Scan"
Post a Comment